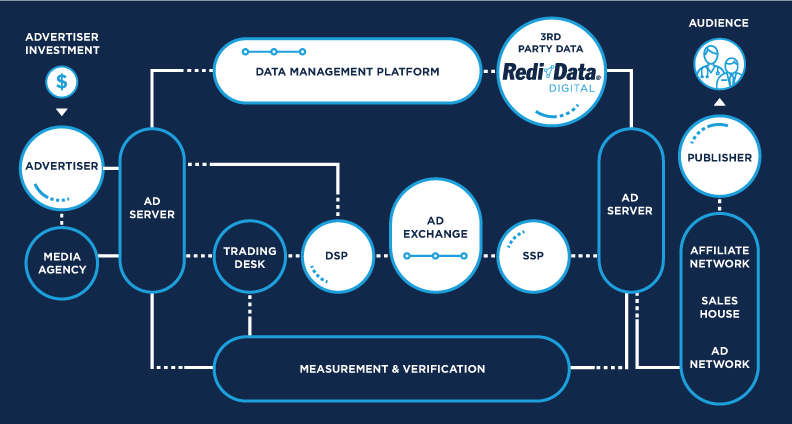
Programmatic advertising has transformed the digital advertising landscape, offering advertisers a more efficient, targeted, and data-driven approach to buying ad space. In ad networks, programmatic advertising plays a pivotal role in streamlining the ad buying process, enhancing the precision of targeting, and maximizing return on investment (ROI). This article explores the key aspects of programmatic advertising within ad networks and how it benefits both advertisers and publishers.
1. What is Programmatic Advertising?
1.1 Understanding Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising refers to the automated buying and selling of digital ad space using software and algorithms. Unlike traditional methods that involve manual negotiations and orders, programmatic advertising allows for real-time transactions and dynamic ad placements.
- Automation: Programmatic advertising uses software to automate the ad buying process, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Real-Time Bidding (RTB): A core feature of programmatic advertising, RTB allows advertisers to bid on ad impressions in real-time, ensuring that ads are shown to the right users at the right time.
1.2 Types of Programmatic Advertising
There are several types of programmatic advertising, each serving different needs and objectives.
- Open Auctions: Also known as open exchanges, these are real-time auctions where multiple advertisers bid on available ad impressions.
- Private Marketplaces (PMPs): Invite-only auctions where premium publishers offer ad inventory to select advertisers.
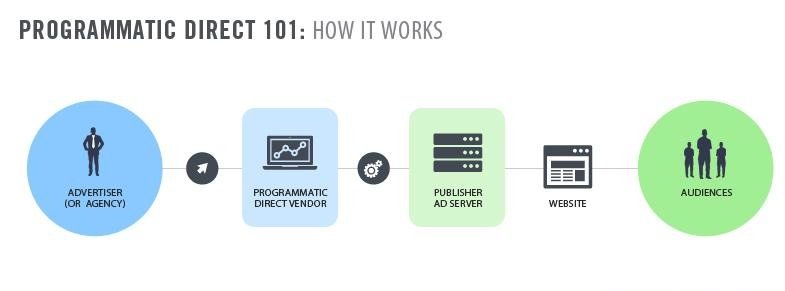
- Programmatic Direct: A direct deal between advertisers and publishers without the need for auctions, often used for high-value or guaranteed placements.
The Role of Programmatic Advertising in Ad Networks
2. How Programmatic Advertising Enhances Ad Networks
2.1 Improved Targeting Capabilities
One of the biggest advantages of programmatic advertising within ad networks is the ability to deliver highly targeted ads.
- Data-Driven Targeting: Programmatic platforms use vast amounts of data, including demographic, behavioral, and contextual information, to target ads more precisely.
- Personalization: Advertisers can create personalized ad experiences by targeting specific audience segments based on their interests, behaviors, and previous interactions.
2.2 Increased Efficiency
Programmatic advertising significantly increases the efficiency of ad campaigns by automating the buying process and optimizing ad placements in real-time.
- Automation: By eliminating manual processes, programmatic advertising reduces the time and effort required to manage campaigns, allowing advertisers to focus on strategy and creativity.
- Real-Time Optimization: Programmatic platforms continuously analyze performance data and adjust bids, placements, and targeting in real-time to maximize results.
2.3 Cost-Effectiveness
Programmatic advertising can be more cost-effective than traditional methods due to its precision targeting and real-time bidding capabilities.
- Reduced Wastage: By targeting only the most relevant audiences, programmatic advertising minimizes ad spend on uninterested or irrelevant users.
- Competitive Pricing: Real-time bidding ensures that advertisers pay the market rate for ad impressions, preventing overpayment and improving ROI.
3. The Role of Ad Networks in Programmatic Advertising
3.1 Connecting Advertisers and Publishers
Ad networks play a crucial role in programmatic advertising by serving as intermediaries that connect advertisers with publishers. They provide the infrastructure and platforms needed for programmatic transactions to take place.
- Inventory Access: Ad networks aggregate ad inventory from multiple publishers, giving advertisers access to a wide range of websites and apps.
- Technology Integration: Many ad networks have integrated programmatic platforms, such as demand-side platforms (DSPs) and supply-side platforms (SSPs), to facilitate automated buying and selling.
3.2 Ensuring Transparency and Brand Safety
With the rise of programmatic advertising, transparency and brand safety have become key concerns. Ad networks address these issues by implementing strict standards and technologies to protect advertisers.
- Ad Fraud Prevention: Ad networks use advanced technologies to detect and prevent ad fraud, ensuring that advertisers’ budgets are not wasted on fake impressions or clicks.
- Brand Safety Measures: Networks employ tools and strategies to ensure that ads are not placed on inappropriate or harmful content, protecting the advertiser’s brand reputation.
3.3 Data and Analytics
Ad networks provide valuable data and analytics tools that help advertisers monitor and optimize their programmatic campaigns.
- Performance Tracking: Advertisers can track key metrics such as impressions, clicks, conversions, and ROI in real-time, allowing for continuous optimization.
- Audience Insights: Networks offer detailed insights into audience behavior and preferences, enabling more effective targeting and campaign strategies.
4. Challenges and Considerations in Programmatic Advertising
4.1 Complexity and Learning Curve
While programmatic advertising offers numerous benefits, it can be complex and requires a certain level of expertise to manage effectively.
- Technical Knowledge: Advertisers need to understand how programmatic platforms work and how to use them to their advantage.
- Continuous Learning: The programmatic landscape is constantly evolving, requiring advertisers to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies.
4.2 Ad Fraud and Viewability Issues
Despite advances in fraud prevention, ad fraud and viewability remain challenges in programmatic advertising.
- Bot Traffic: Advertisers must be vigilant against bot traffic that generates fake impressions or clicks.
- Viewability Standards: Ensuring that ads are actually seen by users (rather than being hidden or scrolled past) is essential for maximizing ROI.
4.3 Data Privacy and Compliance
As programmatic advertising relies heavily on data, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations is critical.
- GDPR and CCPA Compliance: Advertisers must ensure that their data collection and usage practices comply with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
- User Consent: Obtaining and managing user consent for data collection is essential for maintaining trust and legal compliance.
Conclusion
Programmatic advertising has revolutionized the way ad networks operate, offering advertisers unparalleled efficiency, targeting, and ROI. By leveraging data-driven strategies and automated processes, programmatic advertising allows businesses to reach their target audiences more effectively while optimizing their ad spend. However, as with any technology, it comes with challenges that require careful management. By understanding the role of programmatic advertising in ad networks and addressing potential pitfalls, advertisers can fully harness its power to achieve their marketing goals.
