Ad networks play a crucial role in the digital advertising ecosystem, acting as intermediaries that connect advertisers with publishers. These platforms simplify the process of buying and selling ad space, making it easier for advertisers to reach their target audiences while enabling publishers to monetize their content. In this article, we’ll break down how ad networks work, the different types available, and the benefits they offer to both advertisers and publishers.
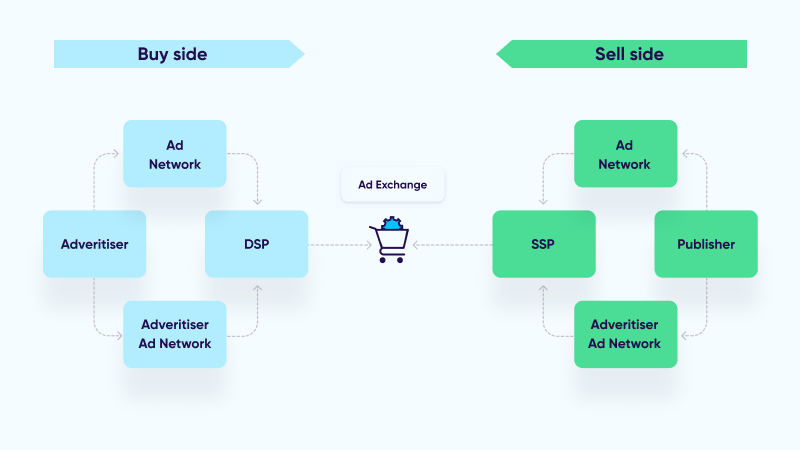
1. What Are Ad Networks?
1.1 Definition and Purpose
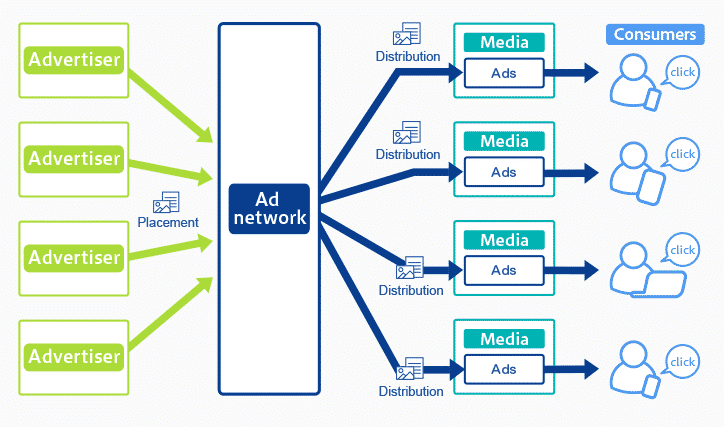
An ad network is a platform that aggregates ad inventory from publishers and matches it with the demand from advertisers.
- For Advertisers: Ad networks provide access to a large pool of ad inventory across multiple websites, allowing advertisers to reach a broad or targeted audience.
- For Publishers: Ad networks help publishers monetize their content by selling ad space on their websites to advertisers willing to pay for exposure.
1.2 The Role in Digital Advertising
Ad networks streamline the process of buying and selling ad space by automating the matchmaking process between advertisers and publishers.
- Simplified Transactions: Advertisers don’t need to negotiate directly with multiple publishers; instead, they can buy ad space through the network.
- Targeted Advertising: Ad networks often use data to target ads based on user demographics, behavior, or interests, increasing the effectiveness of campaigns.
2. How Do Ad Networks Work?
2.1 The Basic Workflow
The functioning of an ad network can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Ad Inventory Aggregation: Publishers make their ad space available on the network, creating a pool of inventory that can be sold to advertisers.
- Ad Placement: Advertisers set up campaigns within the ad network, specifying their target audience, budget, and other parameters.
- Bidding Process: When a user visits a publisher’s website, the ad network automatically auctions the available ad space to the highest bidder in real-time.
- Ad Delivery: The winning ad is displayed to the user, and the advertiser is charged based on the agreed-upon pricing model (e.g., cost-per-click, cost-per-impression).
- Performance Tracking: The ad network tracks the performance of the ads, providing detailed analytics to both advertisers and publishers.
2.2 Key Components
Ad networks consist of several key components that facilitate the buying and selling of ad space:
- Advertisers: Businesses or individuals looking to promote their products or services through online ads.
- Publishers: Website owners or app developers who offer ad space on their platforms.
- Ad Inventory: The available ad space across various publisher websites or apps.
- Targeting Data: Information used to match ads with the most relevant audience, such as demographics, location, or browsing behavior.
- Pricing Models: The methods used to charge advertisers for ad placements, including CPC (cost-per-click), CPM (cost-per-thousand-impressions), and CPA (cost-per-acquisition).
3. Types of Ad Networks
3.1 Vertical Ad Networks
Vertical ad networks specialize in specific industries or niches, providing advertisers with highly targeted audiences.
- Industry-Specific Focus: These networks focus on particular sectors such as finance, healthcare, or technology, allowing advertisers to reach a highly relevant audience.
- Higher Engagement Rates: Ads are more likely to resonate with users who are interested in the specific content provided by publishers in the network.
3.2 Horizontal Ad Networks
Horizontal ad networks offer a wide range of ad inventory across various industries and niches, providing broad reach.
- Diverse Inventory: These networks aggregate ad space from multiple publishers across different categories, giving advertisers access to a wide audience.
- Mass Market Appeal: Ideal for advertisers looking to reach a broad audience across various interests and demographics.
3.3 Premium Ad Networks
Premium ad networks offer access to high-quality, exclusive ad inventory from well-known publishers.
- High-Quality Placements: Ads are placed on reputable sites with high traffic, ensuring better visibility and brand safety.
- Higher Costs: Due to the premium nature of the inventory, advertisers can expect to pay higher rates for placements on these networks.
3.4 Programmatic Ad Networks
Programmatic ad networks use automated technology to buy and sell ad space in real-time.
- Real-Time Bidding (RTB): Ads are bought and sold through an auction system in real-time, allowing for dynamic pricing and placement.
- Data-Driven Targeting: Programmatic networks use extensive data to target ads more precisely, improving campaign efficiency and ROI.
An Introduction to Ad Networks
4. Benefits of Using Ad Networks
4.1 For Advertisers
Ad networks offer several advantages to advertisers looking to run digital campaigns:
- Scalability: Advertisers can reach a large audience across multiple websites without negotiating with individual publishers.
- Cost-Effective: Automated bidding systems can help advertisers get the best prices for ad placements, maximizing their budget.
- Targeting Capabilities: Advanced targeting options allow advertisers to reach specific demographics, increasing the relevance and impact of their ads.
4.2 For Publishers
Publishers also benefit significantly from partnering with ad networks:
- Monetization Opportunities: Ad networks provide a consistent revenue stream by filling ad space with paid advertisements.
- Reduced Workload: Publishers don’t need to manage direct relationships with advertisers, as the network handles sales and placements.
- Access to Diverse Advertisers: By joining an ad network, publishers can attract a wide range of advertisers from various industries.
5. Challenges and Considerations
5.1 Ad Fraud
Ad fraud is a significant concern in the digital advertising space, where fraudulent clicks or impressions can waste advertisers’ budgets.
- Preventive Measures: Ad networks often employ technologies such as bots and filters to detect and prevent fraudulent activity.
- Transparency: Advertisers should seek networks that provide clear and transparent reporting to ensure they’re getting genuine interactions.
5.2 Brand Safety
Ensuring that ads appear alongside appropriate content is crucial for maintaining brand reputation.
- Content Control: Premium ad networks offer better control over ad placements, reducing the risk of ads appearing on questionable sites.
- Brand Safety Tools: Many networks offer tools and services to help advertisers ensure their ads are placed in a safe and relevant context.
Conclusion
Ad networks are essential components of the digital advertising landscape, providing a streamlined and efficient way for advertisers to reach their target audiences and for publishers to monetize their content. By understanding how ad networks work, the different types available, and the benefits they offer, both advertisers and publishers can make informed decisions to optimize their digital advertising strategies. As the digital space continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and technologies in ad networks will be key to success.
